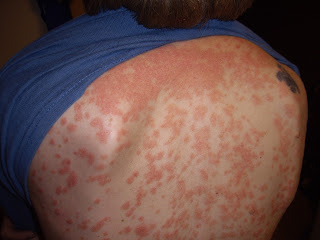
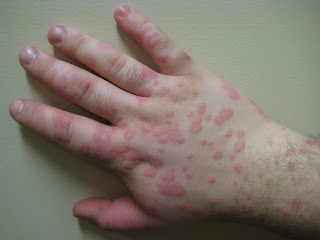
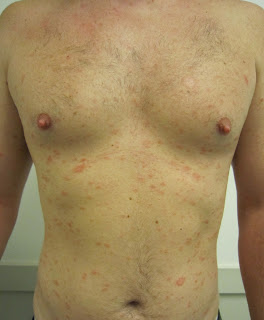
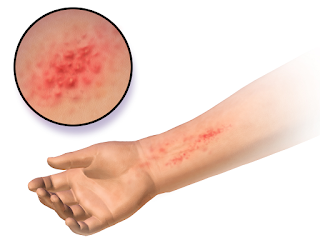
Baby Eczema - Eczema (also called atopic dermatitis) is a skin rash, which most of the time comes out sometime during the first five years of a child's life. Eczema in babies appears usually on the cheeks or the scalp, although you can extend to your arms, legs, chest or other parts of the body.
The eruption could manifest itself as dry, thick and scaly skin or could consist of very small red granite, which can produce blisters, ooze or become infected if you scratch them. Scratching may cause scabs, darkening the skin as well as long-term scars.
Usually eczema comes and goes. It is not contagious, but it produces an intense itch, it may be quite uncomfortable. Scratching so it can become a problem. If this condition is left untreated, the rash may be a little wrong.
The doctor can diagnose eczema to examine your baby's skin. It is possible that you refer to a dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis and to provide adequate treatment.
What causes eczema?
Although not known with certainty what the cause, what is known is that eczema is usually hereditary. Therefore, it is more likely that your baby has it if you or any other members of your family have had eczema, asthma or allergies.
Eczema is an allergic reaction to something, but they cause allergens or irritants in the environment of your baby (such as pollen or cigarette smoke). Although the impact is lower, feeding your child can also cause eczema. Even your own diet, if you are breast-feeding a baby.
 |
| Baby Eczema - How To Treat Baby Eczema |
The heat, the irritants that come into contact with the skin of the baby (such as wool or the chemicals have some soaps,
lotions or detergents), changes in temperature and dry skin can also aggravate eczema. Stress can also cause an outbreak of eczema.
How common is eczema?
About 20 percent of infants and young children has eczema. Usually occur in early childhood: 65 percent of patients develop symptoms in the first year of life, and 90 percent show symptoms before age 5.
It is impossible to know in advance if your child eczema be eradicated for ever. Fortunately, the condition usually becomes less intense with age. In many children, eczema disappears before 2 years of age, and in others, persists into adulthood.
What I do to treat my baby eczema?
A good care of your skin is crucial. Then we offer you some tips:
- Skin care
- Baths and hydrating lotions
Ask the doctor how many times you should bathe your baby. Many specialists believe that the daily bath can be beneficial for babies with eczema. But avoid very hot water because it dehydrates the skin faster than warm water.
Use mild soaps, and wash the head and body when you're finish bathing him so he is sitting in soapy water. Once you take out of the tub, her skin gently dry with towel, without rubbing it.
Then, while your skin is still wet, immediately you moisturizing and emollient products in abundance: an ointment, cream or lotion that "seal" own moisture from the body in your baby's skin. Ointments and creams contain more emollient and less water than lotions, so they are usually the best option for children with eczema.
"I recommend emollient creams for children of all ages," says Michael Smith, an associate professor of medicine and Pediatrics in the division of Dermatology of the Vanderbilt Medical Center in Nashville, in Texas. The expert recommends that, by applying emollient for the first time, do it for a short period of time, to make sure that it does not irritate your baby's skin.
Smith suggests that the most effective treatment to treat eczema is moisturize and lubricate the skin at the same time, by applying an emollient cream on damp skin. The emollient solution will not improve, red, inflamed areas and causing itching but will help rehabilitate the invisible layer that protects the skin. (This protective barrier, which is part of the normal outer layer of skin, damaged in children suffering from eczema).
Let your child's skin to breathe and keep fresh
Dress your baby with soft natural fabrics such as cotton. But avoid wool and other rough material because they can irritate your skin. Do not put overdress your baby or cobijes it more than necessary, since it is important to avoid overheating.
Soaps and bath it
Use soft and without perfume, or those being developed especially for sensitive skin soaps and shampoos. It also uses detergents that are soft and without perfume when you wash clothing and bedding for your baby. Do not use fabric softener.
Avoid scratching
Possibly your baby try to find relief scratching with hands or rubbing the face with the sheet when you sleep. But scratching or scrubbing it can irritate or inflame your skin even more and worse.
Put in the crib or bed softer savannah that you have, and keep your nails short. Do you sleep with mittens or SOCKS cotton in your hands, if you can tolerate them. If you have difficulty sleeping due to eczema, talk to your health care provider. Perhaps suggest you a dose of an antihistamine child that will decrease the itching and will also produce sleep.
It soothes intense episodes of eczema
During an intense episode of eczema you can put cold compresses on the area several times a day, followed by a moisturizer.
Use chlorine or bleach to treat eczema
A study published in the journal Pediatrics, in May 2009, tested treatments to relieve eczema in children who suffered from severe cases of this condition. The children were between 6 months and 17 years of age.
The researchers found that adding a little bit of chlorine in the bath tub and soak there children with ezcema, five to 10 minutes, two times a week, was much more effective to treat this condition, that soak them with pure water. The improvement was so notorious that the researchers decided to stop the study at an early stage, so that the children were bathed with water, will also benefit from treatment with chlorine.
If your baby has moderate to severe eczema, you may try the chlorine treatment, particularly if your child develops infections on the skin. Thus recommended it Amy Paller, one of the authors of that study, and Walter J. Hamlin, head of the Department of Dermatology and Professor of Pediatrics at the school of medicine Feinberg of Northwestern University. But remember that before using this method, it is very important to have the doctor's approval.
Paller recommendation is to add two teaspoons of chlorine per each gallon of water containing bath tub (or half a cup of chlorine if the bathtub is full), at least two times a week. It is crucial that you follow these tips:
Make sure that your baby does not drink water.
Scattered the chlorine in the water before placing the child in the bathtub (is fundamental to prevent undiluted chlorine from penetrating the skin of your little).
Nashville, Smith, pediatrician is in accordance with the recommendation of Paller. 'Use a little chlorine to treat eczema is safe and easy,' he says. "It is basically as if you meddle to the child in a pool that has just been you add chlorine, which is used to remove bacteria. Treatment with chlorine is very useful for children who have recurrent infections related to eczema, but also has proven to be effective to simply eliminate bacteria, allowing easy eczema treatment".
The suggestion of Smith is to use 1/3 to 1/2 cup of chlorine when the tub is full of water or 1 teaspoon per gallon of water. It also recommends to give a brief bath the child after having been a time in the tub, to remove the smell of chlorine.
To prevent the water diluted chlorine in your child's mouth or eyes, Smith recommended not to wash the face. Your suggestion is to apply in the baby's face an ointment or petrolatum ointment to protect the face skin from irritants such as saliva, food and beverages.
The open areas of the face, draining, the expert recommends using antibiotic ointments that are sold without prescription such as bacitracin or a combination that contains polymyxin and bacitracin. If these remedies do not work, call your baby's doctor.
Avoid factors that cause eczema
- Sudden changes in temperature may cause eczema worse, so avoid that your child is hot and then cools too fast and vice versa.
- If it seems that the eczema was caused by environmental allergens, such as seasonal allergies, we recommend that you consult an allergist who will advise you how to treat those allergies.
- Keep your little away from tobacco smoke.
- It seeks to identify and minimize the factors that can cause eczema. Get everything to help your little to manage stress (for example, could offer more opportunities to be calm and relaxed).
Could the eczema that my baby is due to a certain food?
While eczema not a specific allergy is caused by, in some children there are certain foods that can trigger it or make worse it. If you or your doctor suspect that your child eczema has any relationship with certain foods, the main suspects are cow's milk and eggs, followed by soy, wheat, peanuts and fish.
You could try to eliminate these foods from your diet (and your own diet) If you are breast-feeding a baby. Removes the suspected foods one at a time, giving a couple of weeks of testing between one and the other, since it may take up to two weeks that will eliminate the traces of a food of your body.
If you use formula milk and your baby suffers from eczema, the doctor you perhaps suggest you start using a variety of hypoallergenic milk (but not soya). It is not always the solution, but worth a try.
Researchers continue to study the relationship between eczema and food. In a study published in 2007, German researchers discovered a correlation between a high maternal diet margarine, vegetable oils and citrus fruits during the last four weeks of pregnancy and eczema in children younger than 2 years.
Other recent studies suggest that consumption of probiotics (live microorganisms that support the natural balance of the body) during the prenatal period and when the child is a baby, can help prevent the development of eczema in children who have a high risk of contracting it or develop allergies (in families who have older children who have had eczema, for example). Some studies have also shown that probiotics may help reduce the severity of eczema once it has already appeared.
Remember that foods are the main trigger only at around 10 percent of the cases of eczema. Therefore you must also be aware of other factors, such as skin care.
What should I do if the rash does not improve?
Talk to your child's doctor or a dermatologist, pediatrician. If the rash does not improve by following the suggestions that you indicated above, the doctor could tell you that you use soft corticosteroids, which can be purchased without a prescription.
If the medication that is sold without a prescription does not work, the doctor may prescribe a more potent corticosteroids. Applying this cream or ointment sometimes is very effective to interrupt a cycle of persistent eczema.
Researchers are developing new drugs to help patients with eczema. So if your baby still struggling with this problem, check with the doctor so you report on these new drugs.
Call the doctor if the fever rises in your baby either if it shows other signs that an infection could have (the area is hot to the touch or oozing or if their bark is yellow, for example).
If your baby goes to kindergarten, talk with people who care what about eczema. Explain that the condition is not contagious but that other children could make jokes on the subject.
You can read another articles like
What Is Eczema,
Atopic Eczema.
baby eczema treatment
baby eczema on face
eczema baby